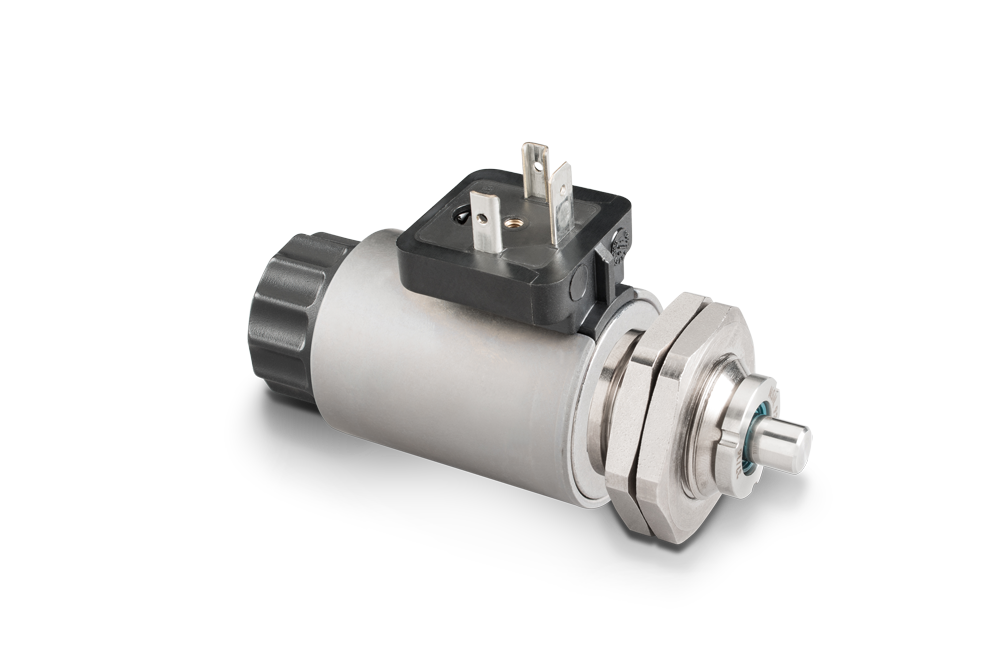
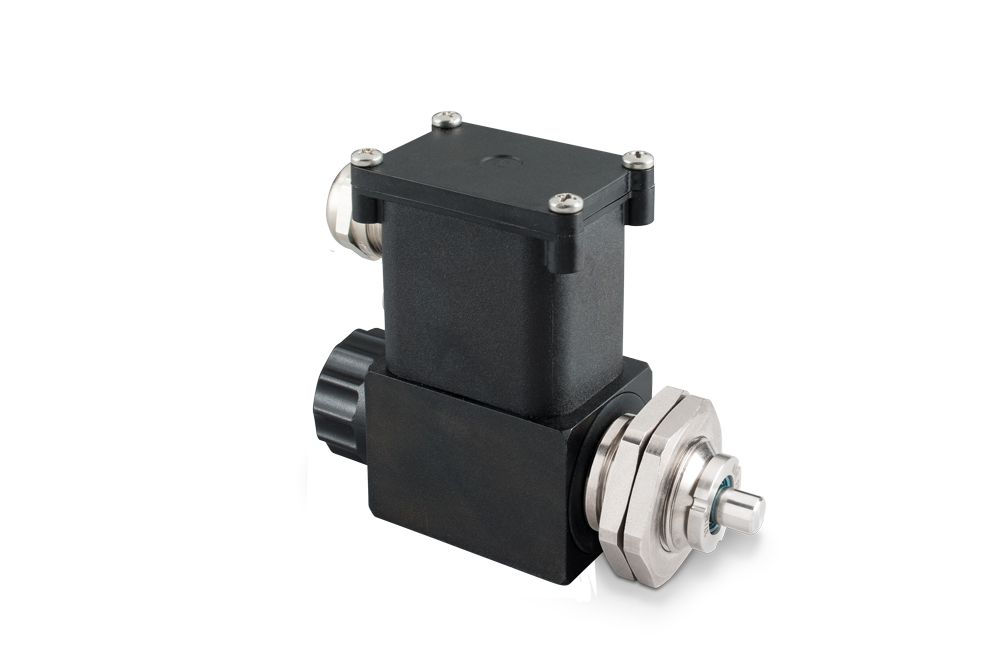
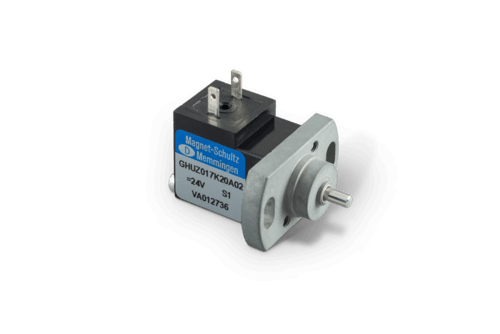
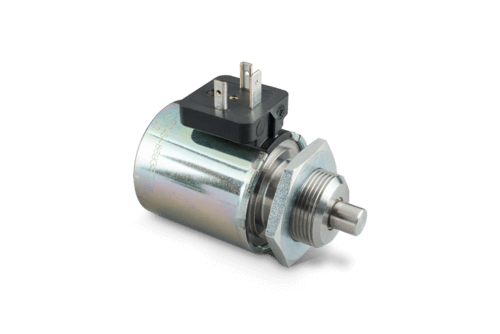
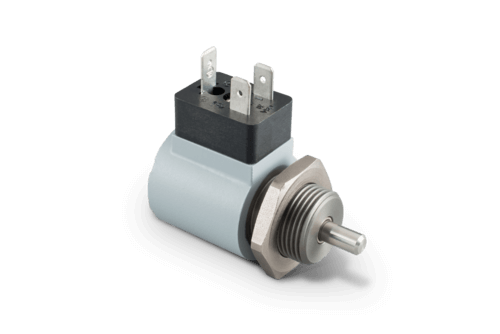
Shotbolt Lock Units
You want to lock a gate, a door or a flap or you want to prevent them from unintended or unauthorized actuating? A lever or other manual operating device shall be blocked or released?
Our shotbolt lock units and solenoids are your solution.
We offer push type and pull type versions as well as types with limit switch for position detection of the shotbolt.
FAQ Shotbolt Lock Units
What are the special features of a shotbolt lock unit?
A shotbolt locking unit is a single acting solenoid devised for locking duties. The distinctions with respect to single acting solenoids are:
- The design of the armature
- The load capacity of bearing
- The installation of a return spring
At the end of the armature and/or armature rod ,shotbolt locking units have a locking bolt. This bolt can absorb defined lateral forces. This is the reason why the bolt’s and/or the armature’s bearing is dimensioned correspondingly. A return spring defines the locking bolt position in de-energized state. If the locking unit is separated from the supply voltage, the spring moves the armature as well as the connected locking bolt into starting position. This procedure is also called spring reset.
Which are the advantages of electromagnetic locking systems compared to other solutions?
Electromagnetic locking systems absorb substantial lateral forces. Please refer to our technical data sheets for the values. Since the locking bolt’s drive is directly carried out by the solenoid armature without interim transmission, short switch times and a high functional reliability can be achieved.
How to select locking units
A locking unit‘s important characteristic is the stroke, the distance covered by the locking bolt when fed with current, and the admissible lateral force. When selecting the locking unit, it must be observed that the factual lateral force remains below the admissible lateral force.
Dependent on the individual case, either pulling (locked without current) or pushing (unlocked without current) models can be selected. If the position of the locking bolt is to be monitored, the use of a version with signal switch is recommended.
What is the difference between pulling and pushing model and when are they applied?
Pulling versions have the locking bolt extended by spring tension in idle position. If the device is charged by supply voltage, the bolt is withdrawn. Pushing versions operate the other way round. The locking bolt is held in the device by a spring in de-energized state. When energized, it is pushed out of the device.
As a conclusion, the decision for the respective model depends on the application and its relevant demands. As a first orientation, we recommend weighing the answers to the following questions, taking into account safety-relevant, functional and energetic aspects:
- What needs to be locked, with which aim?
- Which state does the locking need to take up in case of power failure? Does the shotbolt locking unit have to be closed or open in this case?
- Are there standards stipulated by relevant regulations?
- How long does the locking system have to be energized in order guarantee the desired function?
- In case of continuous energization, it must be observed that the locking unit’s surface heats up, which can be remedied by using a holding current reduction.
MAGNET-SCHULTZ GmbH & Co. KG